Vehicle accessories
Any vehicle accessory must:
- be securely fitted without increasing the risk of injury to any person or
- not impede the safe control of the vehicle or
- not affect the vehicle being roadworthy.
Lights
Vehicles must be fitted with at least two main beam headlamps to illuminate the road over a long distance ahead of the vehicle.
You need at least one main beam headlamp on a motorcycle.
Up to four main beam headlamps may be fitted to a vehicle.
Additional lights
Additional lighting such as driving lamps, fog lamps and search lamps may be fitted to vehicles in the Northern Territory (NT).
Any additional driving lamps, fog lamps or work lamps fitted to a vehicle must be designed and securely fitted in a way that:
- minimises the likelihood of injury to a person making contact with the vehicle
- does not obstruct the driver's view of the road and traffic to the front of the vehicle
- does not compromise the vehicle's compliance with the Australian Vehicle Standards Rules and Australian Design Rules.
Australian Standards and Australian Design Rules for additional lights
- ADR 13/00 installation of lighting and light-signalling devices on other than L-group vehicles
- ADR 19/xx installation of lighting and light-signalling devices on L-group vehicles
- ADR 46/00 headlamps
- ADR 51/00 filament lamps
- ADR 54/00 headlamps for mopeds
- ADR 55/00 headlamps for motor cycles
- ADR 67/00 installation of lighting and light-signalling devices on three-wheeled vehicles
- ADR 75/00 headlamp cleaners
- ADR 77/00 gas discharge headlamps
- ADR 78/00 gas discharge light sources.
High beam driving lamps (spotlights)
You can fit a combination of up to eight main beam and driving lamps (spot lights) to a vehicle (except motorcycles).
There are no overall height restrictions to the mounting position of a driving lamp, however the driver needs to have a clear view of the road ahead.
The driver's view should not be obstructed by a driving light on a bumper, bull bar or nudge bar.
The driving lamp/s must be in the same position on both sides of the vehicle.
An LED light bar may be mounted as a single lamp and must be mounted in the centre of the vehicle.
All driving lamps must turn off when the vehicle's main beam headlamps are switched to dipped beam or low beam.
Fog lamps
You can fit two fog lamps to a vehicle with at least four wheels. The lights must be mounted according to all of the following:
- symmetrically
- not more than 400mm from the sides (extreme outer edge) of the vehicle
- at least 600mm apart
- not less than 250mm above the ground so the top of the beam is not higher than the centre of the fog lamp, when measured eight metres in front of the vehicle.
Fog lamps must be able to be operated independently from the headlights and driving lamps. As a minimum, they must only be able to operate when the park lamps are on.
Search or work lamps
Additional lamps can be used for temporary purposes such as any of the following:
- reading of signs
- handling or adjusting of loads
- providing additional illumination in off-road situations.
These lights may be fitted to a vehicle in any location on the vehicle.
High output light source lamps
The below information helps to explain high output light source lamps when fitted as replace lamp assemblies to a dipped beam (low beam) circuit as an in-service vehicle modification.
As light technology advances away from tungsten and halogen lamps and production costs decrease, some vehicle manufacturers/Original Equipment Manufacturers (OEM) are offering high output dipped beam headlamp as standard equipment.
New light source technology includes:
- “Gas-discharge light source" - a light source where the element for visible radiation is a discharge arc producing electro-luminescence/fluorescence (i.e. Xenon, Bi-Xenon – up to 3 times brighter than halogen).
- "Light-emitting diode (LED) light source" - a light source where the element for visible radiation is one or more solid state junctions producing injection-luminescence/fluorescence (low heat generation).
- Laser – a light source where a blue laser excites yellow phosphorus producing an intense white light (up to 2 times brighter than high intensity discharge (HID) lamps).
Lamp requirements
Under Australian Design Rules (ADR), requirements for high output light source lamps and assemblies include self-levelling and headlamp cleaning devices for lamps producing more than 2000 lumens (a measure of light output).
Retro-fitting lamps
Retro-fitting original headlamps with non-ADR complying aftermarket globes or non-standard lamp assemblies to the dipped beam (low beam) circuit of a vehicle does not guarantee that the headlamp will comply with the specific set of ADR performance requirements. This could render the vehicle unsuitable for road use.
Vehicles found with non-complying lighting may be defected or refused registration in the NT.
High output light source conversion kits
Aftermarket LED replacement globes and headlamp assemblies advertised for “Off Road Use Only” are not ADR compliant and are not suitable for on-road use.
Aftermarket kit manufacturers or suppliers must provide evidence that replacement lamps comply with the ADRs if:
- the conversion kit fits into the original manufacturer equipment (OEM) headlamp housing in place of the original dipped beam (low beam) lamp and
- there is no change to the headlamp lens, reflector or housing.
You must apply to the Motor Vehicle Registry (MVR) for approval to fit high output light source dipped beam (low beam) lamps to your vehicle.
Before your modification can be approved, you will need to provide the MVR with certification evidence from a qualified Chartered Professional Engineer (CPEng) or approved engineering signatory that the lights comply with the ADR requirements listed below.
Australian Standards and Australian Design Rules for lamps
Lamps must be certified to comply with the following ADRs:
- ADR 13/00 installation of lighting and light-signalling devices on other than L-group vehicles
- ADR 19/xx installation of lighting and light-signalling devices on L-group vehicles
- ADR 46/00 headlamps
- ADR 51/00 filament lamps
- ADR 54/00 headlamps for mopeds
- ADR 55/00 headlamps for motor cycles
- ADR 67/00 installation of lighting and light-signalling devices on three-wheeled vehicles
- ADR 75/00 headlamp cleaners
- ADR 77/00 gas discharge headlamps
- ADR 78/00 gas discharge light sources.
How to apply
To get approval of your lamps so that your vehicle can remain registered, you will need to submit engineering certification to the MVR.
Window tinting standards
The light clarity of a window on vehicles is referred to as luminous transmittance (LT).
If you apply a coating or tint on the driver and front passenger side windows, the windows must have an LT of at least 35%.
A coating or tint applied rearward of the driver's seating position must have an LT of at least 15%.
Any coating or tint applied to vehicle windows and windscreens must be non-reflective and must not have any distortion or bubbling.
Glazing used in the front windscreen of a motor vehicle must have an LT of at least:
- 75% for a vehicle built after 1971
- or 70% for another vehicle.
You can apply a strip with any LT to the following areas of a windscreen:
- the area above the highest point of the windscreen that is swept by a windscreen wiper
- or the upper 10% of the windscreen.
No other coating or tinting is allowed on the windscreen.
Glazing in the interior of a light vehicle must have a LT of at least 70%.
Bicycle racks, roof racks and load-carrying devices
Bicycle racks
A bicycle carrying rack is usually fitted to the tow bar or boot of a vehicle, or the roof rack.
You must do all of the following:
- attach the bicycle rack according to the manufacturer's instructions
- make sure welding on the bicycle rack fits with Australian standards
- secure the tow bar or roof rack and its load
- secure the bicycle to the rack
- make sure the the bicycle rack is free of sharp edges and protrusions.
Rules for fitting a bike rack
You must make sure the bicycle rack and its load does not do any of the following:
- project excessively behind the rear of the vehicle
- exceed rear overhang limits (60% of the vehicle's wheel base)
- protrude more that 150mm beyond the extreme width of either side of the vehicle
- block any vehicle lights
- block the driver's vision of the rear of the vehicle
- block the number plate.
If the bike rack blocks the view of the number plate you can re-locate the number plate, or place an additional number plate onto the bicycle rack.
You will have to pay a fee for the extra number plate, and it must be identical to the number plate on the vehicle.
You should also remove the bike rack from your vehicle when not using it to carry bikes.
Roof racks (ladder racks)
Rules for fitting a roof rack
Ladder racks positioned forward of the windscreen should not do any of the following:
- project more than 150mm from each side of the vehicle or make the vehicle more than 2.5m wide
- obscure any lights – or an additional light must be fitted or the original light must be relocated
- have any sharp edges or protrusions on supports, braces and brackets
- interfere with a person's access to the vehicle.
Ladder racks should be removed when not in use.
Bicycle carrying racks and rear-mounted carrying devices
Any load-carrying device that is roof mounted, towbar-mounted or mounted to the rear of a vehicle must comply with requirements.
Load-carrying devices may include:
- bicycle carrying racks - roof and towbar-mounted
- wheelie bin carriers - towbar-mounted.
Requirements for all load-carrying devices
You must follow all of these requirements when using load-carrying devices:
- make sure the load-carrying device is fit for purpose and is fitted and used in accordance with the manufacturer’s instructions
- all welding carried out in the manufacture of a steel load-carrying device must follow Australian / New Zealand Standard, AS/NZS 1554.1 Structural Steel Welding - Welding of Steel Structures
- the load-carrying device must be secure and suitable for its load
- make sure the load is adequately secured to the load-carrying device when transporting and that the load-carrying device is adequately secured to the vehicle
- make sure the load-carrying device and its attachment to the vehicle is suitable for the weight of the load
- make sure the load-carrying device is free of sharp edges and protrusions.
Lighting visibility requirements
You must make sure the load-carrying device does not obscure your vehicle's lights. You may need additional lighting such as a removable light board.
Number plate visibility requirements
Make sure your number plate is not obscured.
You may need to relocate the number plate when using a load-carrying device or get an additional number plate from an MVR office.
If you relocate your number plate or fit another number plate you should consider a number plate light.
Driver vision and safety requirements
Make sure you can see the rear of the vehicle.
The load-carrying device should be removed when not being used to reduce potential hazards to other road users.
Requirements for rear-mounted load carrying devices
There are additional requirements to the above for rear-mounted load carrying devices.
Make sure the load-carrying device and it's load does not:
- project excessively behind the rear of the vehicle
- exceed rear overhang limits - 60 per cent of the vehicle's wheelbase
- protrude more than 150mm from the width of either side of the vehicle.
Antennas
You should only mount large base radio antennas on the front of your vehicle if it is impossible or impractical to install the antenna to the rear of the vehicle.
The antenna must be attached to the left side and as low as possible.
Only one large base antenna may be fitted to the front of the vehicle. The maximum diameter permitted is 75mm.
The antenna must not:
- have any sharp edges or protrusions
- obscure any light - additional lights must be fitted or the original light relocated if a light is blocked.
Bonnet scoop
Bonnet scoops or projections may be fitted to a vehicle provided the driver's vision is not restricted.
Bonnet-mounted scoops or projections must meet the following requirements:
- When a 165mm diameter sphere is placed on the bonnet in front of the scoop (or bonnet projection) and rolled backwards until it touches the scoop, no forward point of the scoop or point of contact between the sphere and the scoop must lie above a horizontal plane passing through the centre of the sphere.
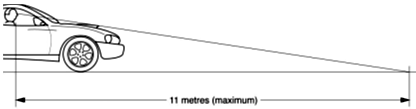
- It must be possible to see either the surface of the road 11m in front of the driver's eye or all of the front edge of the body when looking across the top of the bonnet scoop.
- The edges at the front of a scoop must be well rounded with a minimum of 10mm radius.
- The scoop must not have reflective surfaces that will cause glare towards the driver.
- A bonnet scoop manufactured from a plastic or fibre glass material may be fitted, providing that the hole in the original bonnet does not reduce the strength or impact resistance of the bonnet or a rigid component – eg: an air cleaner or carburettor.
- Holes may be cut in the bonnet and the protrusion of an air cleaner or carburettor above the bonnet line, but below the bonnet scoop providing that the bonnet scoop or raised bonnet section is manufactured from equivalent gauge mild steel, compared with that of the original bonnet.
- If any bonnet reinforcing braces are cut or modified, the design of the modified bonnet must be of equal strength to the original bonnet and any sharp edges created must be suitably treated.
- All edges and corners shall have a radius of not less than 5mm and of general design and construction to reduce to a minimum the risk of bodily injury to any person.
Bull bars
Bull bars must be designed and fitted so that the safety of the vehicle is not adversely affected.
A bull bar must include all of the following:
- securely mounted and supported
- free of sharp protrusions and all exposed sections of the bull bar and fittings must be radiused and de-burred
- have extra lights fitted, according with Australian Design Rules, if it obscures any light
- matte black on surfaces that could reflect light from the vehicle's headlights.
It must not be any of the following:
- a danger to other road users
- obstruct the vision of the driver
- project further from the front of the vehicle than is necessary for its attachment. Bull bars should not add a significant load to the front suspension.
- obscure any light – including indicator lights at all viewing angles.
Vehicles fitted with an airbag or manufactured with full frontal impact occupant protection must only be fitted with a bull bar that has been:
- certified by the vehicle manufacturer as suitable for that vehicle
- or certified by the manufacturer as complying with the Australian Design Rules and doesn't interfere with the airbag timing mechanism.
Bull bars that comply with Australian standards 4876.1-2002 provide a higher level of pedestrian protection.
Fishing rod holders
When fitting a fishing rod holder, you must follow all of the below:
- the fitting allows the driver to see the road and traffic to the front and sides of the vehicle
- the vehicle's lighting isn't obstructed by rods or holders
- rod holders are either removed when they are not in use or retracted behind the bull bar with no protruding surfaces.
Gauges
Any additional internal or external gauges must be safely fitted and not do any of the following:
- interfere with the field of view of the driver
- produce glare to the driver
- have the possibility of an oil pressure line breaking with pressurised fluids spraying onto the windscreen.
Side skirts, flares and spoilers
Side skirts, front and rear spoilers may be fitted provided road clearance and air flow for brake cooling is not affected.
They must not be fitted so that it is likely to increase the risk of bodily injury to any person.
All material is to be of a suitable thickness and be free from sharp edges or corners.
Rear spoilers must be within the body shape or outline of the mounting surface – e.g. boot outline.
The minimum thickness of end plates is 4mm and they must be free of sharp edges or corners.
Visual display screens
DVD screens, television receivers and visual display units can be installed in a vehicle according to the manufacturer's instructions or Australian Standards.
The screen must not do any of the following:
- obscure the driver's view of the road
- impede the movement of anyone in the vehicle
- interfere with restraint systems such as head restraints, seat belts and airbags.
More information
For more information, read vehicle information bulletins and forms.
Give feedback about this page.
Share this page:
URL copied!